SPI - Serial Peripheral Interface

Example available on GitHub. Check liteboard SPI example.
SPI is a full-duplex, master - slave, synchronous serial interface used mainly used in embedded systems.
|
<uml> ditaa /————–\ /—————\
\————–/ | | | | | | | | /---------------\
| | | | | SPI slave 2 |
| | | | | |
| | | \------>+ SCLK |
| | \-------->+ MOSI |
| \-----------+ MISO |
\------------>+ SS |
| cYEL |
\---------------/
</uml> |
Interface
SPI configurationTo configure SPI interface following parameters must be defined:
|
liteSOM and SPI
|
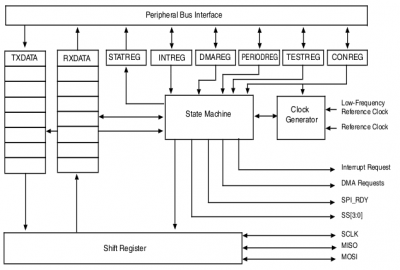
ECSPI block diagram (source: i.MX 6UltraLite Applications Processor Reference Manual) |
Each
Key features of the
|
Device Tree
ecspi1: ecspi@02008000 {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
compatible = "fsl,imx6ul-ecspi", "fsl,imx51-ecspi";
reg = <0x02008000 0x4000>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 31 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
clocks = <&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ECSPI1>,
<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ECSPI1>;
clock-names = "ipg", "per";
status = "disabled";
};
ecspi2: ecspi@0200c000 {
[...]
};
ecspi3: ecspi@02010000 {
[...]
};
ecspi4: ecspi@02014000 {
[...]
};
|
Generic configuration for all four Documentation for all SPI related items configured in this file you can find in fsl-imx-cspi.txt file in the kernel documentation. |
&iomuxc {
pinctrl_ecspi1: ecspi1grp {
fsl,pins = <
MX6UL_PAD_CSI_DATA04__ECSPI1_SCLK 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_CSI_DATA05__GPIO4_IO26 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_CSI_DATA06__ECSPI1_MOSI 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_CSI_DATA07__ECSPI1_MISO 0x1b0b0
>;
};
};
|
SPI @ liteboard pinout To enable SPI on liteboard we have to configure IOMUX Controller to enable SPI pins for this board:
|
&ecspi1 {
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_ecspi1>;
cs-gpios = <&gpio4 26 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>;
status = "okay";
spidev0: spi@0 {
compatible = "spidev";
reg = <0>;
spi-max-frequency = <5000000>;
};
};
|
As a
In this example we will allow userspace application to communicate directly with SPI slave device therefore device tree contains one SPI child node
In addition
To compile -> Device Drivers
-> SPI support
-> User mode SPI device driver support
Please check spi-bus.txt file to check how to configure - via device tree - other SPI parameters. |
Test tools
Buildroot allows you build two SPI test tools:
spidev_test
Buildroot tree location
-> Target packages
-> Debugging, profiling and benchmark
-> spidev_test
Source code
Application source code is available here.
Loopback test
Please connect MISO and MOSI pins together and request spidev_test application to send and then receive default data package via SPI interface.
# spidev_test -D /dev/spidev0.0 -v spi mode: 0x0 bits per word: 8 max speed: 500000 Hz (500 KHz) TX | FF FF FF FF FF FF 40 00 00 00 00 95 FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF F0 0D | ......@....�..................�. RX | FF FF FF FF FF FF 40 00 00 00 00 95 FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF F0 0D | ......@....�..................�.
Other options
Please check application help to see available options.
Usage: spidev_test [-DsbdlHOLC3] -D --device device to use (default /dev/spidev1.1) -s --speed max speed (Hz) -d --delay delay (usec) -b --bpw bits per word -i --input input data from a file (e.g. "test.bin") -o --output output data to a file (e.g. "results.bin") -l --loop loopback -H --cpha clock phase -O --cpol clock polarity -L --lsb least significant bit first -C --cs-high chip select active high -3 --3wire SI/SO signals shared -v --verbose Verbose (show tx buffer) -p Send data (e.g. "1234\xde\xad") -N --no-cs no chip select -R --ready slave pulls low to pause -2 --dual dual transfer -4 --quad quad transfer
spi-tools
Buildroot tree location
-> Target packages
-> Hardware handling
-> spi-tools
Source code
See spi-tools on GitHub.
spi-config
This application can be used to read/set current spidev configuration.
Read current SPI configuration
# spi-config -q -d /dev/spidev0.0 /dev/spidev0.0: mode=0, lsb=0, bits=8, speed=5000000
Set SPI configuration
To configure SPI to use mode = 2 (CPOL=1, CPAH=0) please use following command.
# spi-config -m 2 -d /dev/spidev0.0
Please read application help to see other options.
# spi-config --help
usage: spi-config options...
options:
-d --device=<dev> use the given spi-dev character device.
-q --query print the current configuration.
-m --mode=[0-3] use the selected spi mode:
0: low iddle level, sample on leading edge,
1: low iddle level, sample on trailing edge,
2: high iddle level, sample on leading edge,
3: high iddle level, sample on trailing edge.
-l --lsb={0,1} LSB first (1) or MSB first (0).
-b --bits=[7...] bits per word.
-s --speed=<int> set the speed in Hz.
-h --help this screen.
-v --version display the version number.
spi-pipe
spi-pipe allows you to send and receive data simultaneously.
Send data via SPI interface
To send string foo via SPI interface you can use following command
# echo "foo" | spi-pipe -d /dev/spidev0.0
Read data via SPI interface
To read data received via SPI interface plse use following command
# spi-pipe -d /dev/spidev0.0 < /dev/zero | cat
More options
To see other use cases please check spi-tools README file.