Network interface
i.MX6UL contains Dual-Megabit Ethernet Controller. Below you can see how this peripheral is configured for the liteboard.
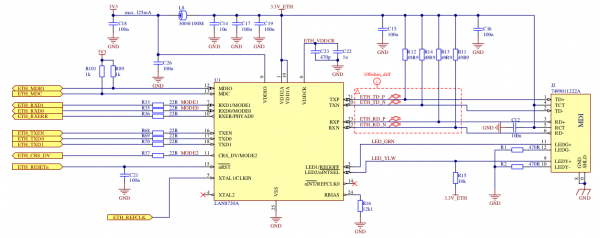
PHY device
|
Liteboard is using external LAN8720A 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX transceiver connected with liteSOM via RMII™ interface. Following signals are required to connect liteSOM with LAN8720A via RMII™:
In addition LAN8720A and liteSOM are connected via SMI signals:
|
Device Tree configuration
fec1: ethernet@02188000 {
compatible = "fsl,imx6ul-fec", "fsl,imx6q-fec";
reg = <0x02188000 0x4000>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 118 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>,
<GIC_SPI 119 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
clocks = <&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET>,
<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET_AHB>,
<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET_PTP>,
<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET_REF>,
<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET_REF>;
clock-names = "ipg", "ahb", "ptp",
"enet_clk_ref", "enet_out";
fsl,num-tx-queues=<1>;
fsl,num-rx-queues=<1>;
status = "disabled";
};
|
Basic configuration for Documentation for this device-tree node you can find in fsl-fec.txt file. |
&fec1 {
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_enet1>;
phy-mode = "rmii";
phy-handle = <ðphy0>;
status = "okay";
mdio {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
ethphy0: ethernet-phy@0 {
reg = <0>;
};
};
};
&iomuxc {
pinctrl_enet1: enet1grp {
fsl,pins = <
MX6UL_PAD_GPIO1_IO07__ENET1_MDC 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_GPIO1_IO06__ENET1_MDIO 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_RX_EN__ENET1_RX_EN 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_RX_ER__ENET1_RX_ER 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_RX_DATA0__ENET1_RDATA00 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_RX_DATA1__ENET1_RDATA01 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_TX_EN__ENET1_TX_EN 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_TX_DATA0__ENET1_TDATA00 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_TX_DATA1__ENET1_TDATA01 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_TX_CLK__ENET1_REF_CLK1 0x4001b031
>;
};
};
|
To enable -> Device Drivers
-> Network device support
-> Ethernet driver support
-> Freescale device
-> FEC ethernet controller (of ColdFire and some i.MX CPUs)
|
Network configuration
Default Buildroot configuration for the liteboard is using DHCP to configure internet connection.
This behavior can be changed via BR2_SYSTEM_DHCP configuration item.
-> System configuration -> Network interface to configure through DHCP
Help
Enter here the name of the network interface (E.G. eth0) to automatically configure through DHCP at bootup. If left empty, no automatic DHCP requests will take place. For more complicated network setups use an overlay to overwrite /etc/network/interfaces or add a networkd configuration file.
If you want to modify /etc/network/interfaces file please read Network Configuration howto from Debian Wiki.
Network status
Current network status you can verify by ifconfig eth0 command
# ifconfig eth0
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 9E:EE:5F:94:B8:D3
inet addr:10.42.0.133 Bcast:10.42.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::9cee:5fff:fe94:b8d3/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:38 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:15 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:5906 (5.7 KiB) TX bytes:1654 (1.6 KiB)
or ip address show eth0
# ip address show eth0
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast qlen 1000
link/ether 9e:ee:5f:94:b8:d3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.42.0.133/24 brd 10.42.0.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::9cee:5fff:fe94:b8d3/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever